Log Mean Temperature Difference Formula
The formula for computing Pearsons ρ population product-moment correlation coefficient rho is as follows 1. Specifically by aggregate split and plyr cast tapply datatable dplyr and so forth.

Heat Transfer L32 P1 Log Mean Temperature Difference Youtube
The more the predicted probability diverges from the actual value the higher is the log-loss value.

. This formula means that you are computing the average of the logarithms of your data and then rescaling that back so the units work out. MRT is a useful concept as the net exchange of radiant energy between two objects is approximately proportional to the product of their. The mean radiant temperature MRT is defined as the uniform temperature of an imaginary enclosure in which the radiant heat transfer from the human body is equal to the radiant heat transfer in the actual non-uniform enclosure.
What does log-loss conceptually mean. Mathematicians have observed that there is usually a difference between the median and the mode and it is 3 times the difference between the mean and the median. Laws of Logarithm base 10.
Mean Mode 3Mean Median Lets take the example of population data based on 50 states. Divide the difference by 18 for formula 2. You can also write x and 10 y.
Specific heat is the amount of thermal energy you need to supply to a sample weighing 1 kg to increase its temperature by 1 KRead on to learn how to apply the heat capacity formula correctly to obtain a valid result. Remember that 59 is also written as 055. Calculate the y value by using the logarithm laws.
The answer to the product is your temperature in Celsius. Sensible temperature refers to the perceived temperature or how hot the weather feels to the average person. In general we know that log 10 xy where x is a real number and x0.
There are many ways to do this in R. This specific heat calculator is a tool that determines the heat capacity of a heated or a cooled sample. Consider the classification problem of spam vs.
Multiply the difference by 59 for formula 1. First take any number to which you want to calculate log 10 value. Log-loss is indicative of how close the prediction probability is to the corresponding actualtrue value 0 or 1 in case of binary classification.
Just use the same code given for Regulate temperature between the optimum range with slight modifications. Your choice of t-test depends on whether you are studying one group or two groups and whether you care about the direction of the difference in group means. Example of First Term and Common Difference of HP.
Where covXY is the covariance of the variables X and Y and σ X sigma X is the population standard deviation of X and σ Y of Y. For instance the mean. The basic difference is that heat is the form of energy that transfers from a hot object to a cold object whereas temperature is the measure of the hotness or coldness of an object.
If you are studying two groups use a. Broadly speaking these problems are of the form split-apply-combine. If you are studying one group use a paired t-test to compare the group mean over time or after an intervention or use a one-sample t-test to compare the group mean to a standard value.
Consider dry heat vs. Mathematically it is defined as the quality of least squares fitting to the original data. Optimum variation is the maximum optimum variation is the minimum Tc optimum optimum value to turn off heater Tc optimum optimum value to turn off fanThe optimum value to turn ON.
Hadley Wickham has written a beautiful article that will give you deeper insight into the whole category of problems and it is well worth reading. The same process is used for the geometric standard deviation confidence intervals interquartile ranges whatever. A calculate the regular statistic on the log data like textSDlog x then rescale back.
The basic 7 different laws of logarithm are mentioned here. His plyr package implements. Yes you can.
The logarithmic mean temperature difference also known as log mean temperature difference LMTD is used to determine the temperature driving force for heat transfer in flow systems most notably in heat exchangersThe LMTD is a logarithmic average of the temperature difference between the hot and cold feeds at each end of the double pipe exchanger. The common difference is denoted as d and it is the same in any progression. If 1a 1b 1c are three terms in Harmonic Progression then the first term is 1a and the common difference is d.
Dividing by 18 will give you the same. At the same air temperature for example 80 degrees. Using the formula given in the article.
In the example of 90 F the answer to the second step for formula 1 is 58 x 05555 3222 C where the 2 is a repeating decimal. The common difference is the difference between any two consecutive numbers in the series. The empirical relationship is expressed in the formula below.
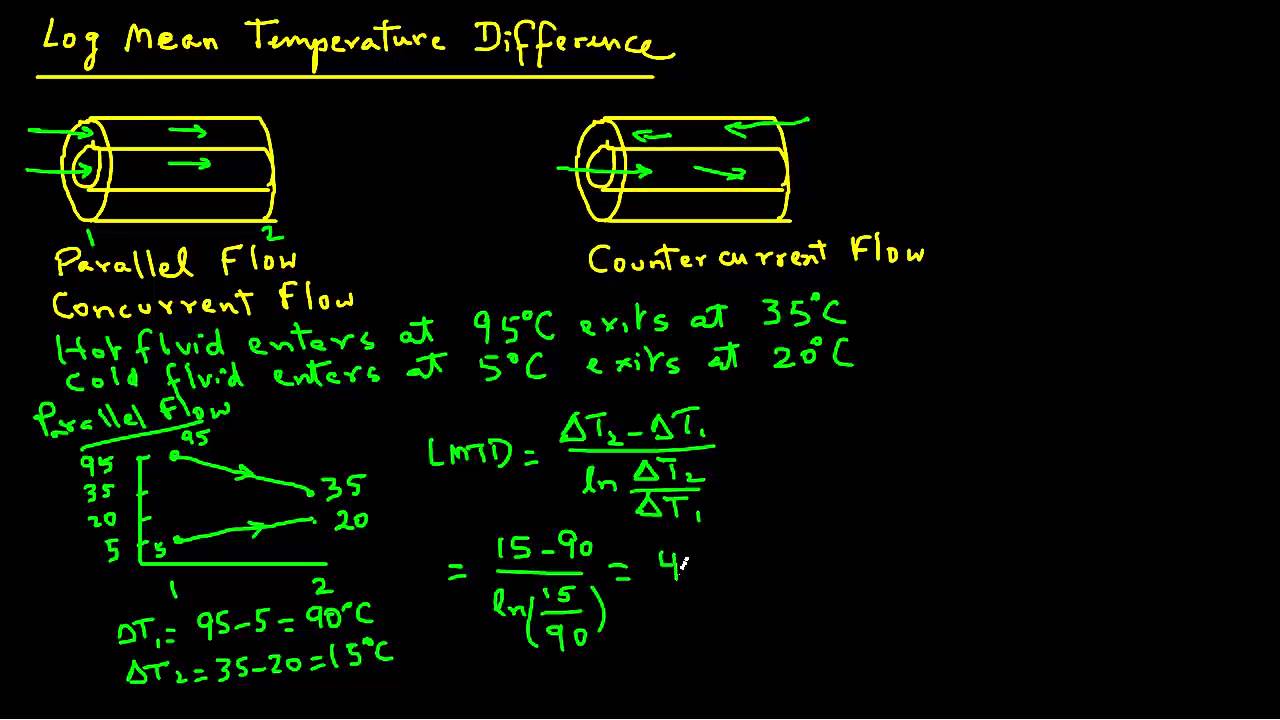
Log Mean Temperature Difference Youtube
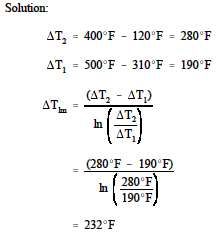
Log Mean Temperature Difference Application Equations For Heat Exchangers

Understanding Lmtd For Heat Exchanger Design Enggcyclopedia
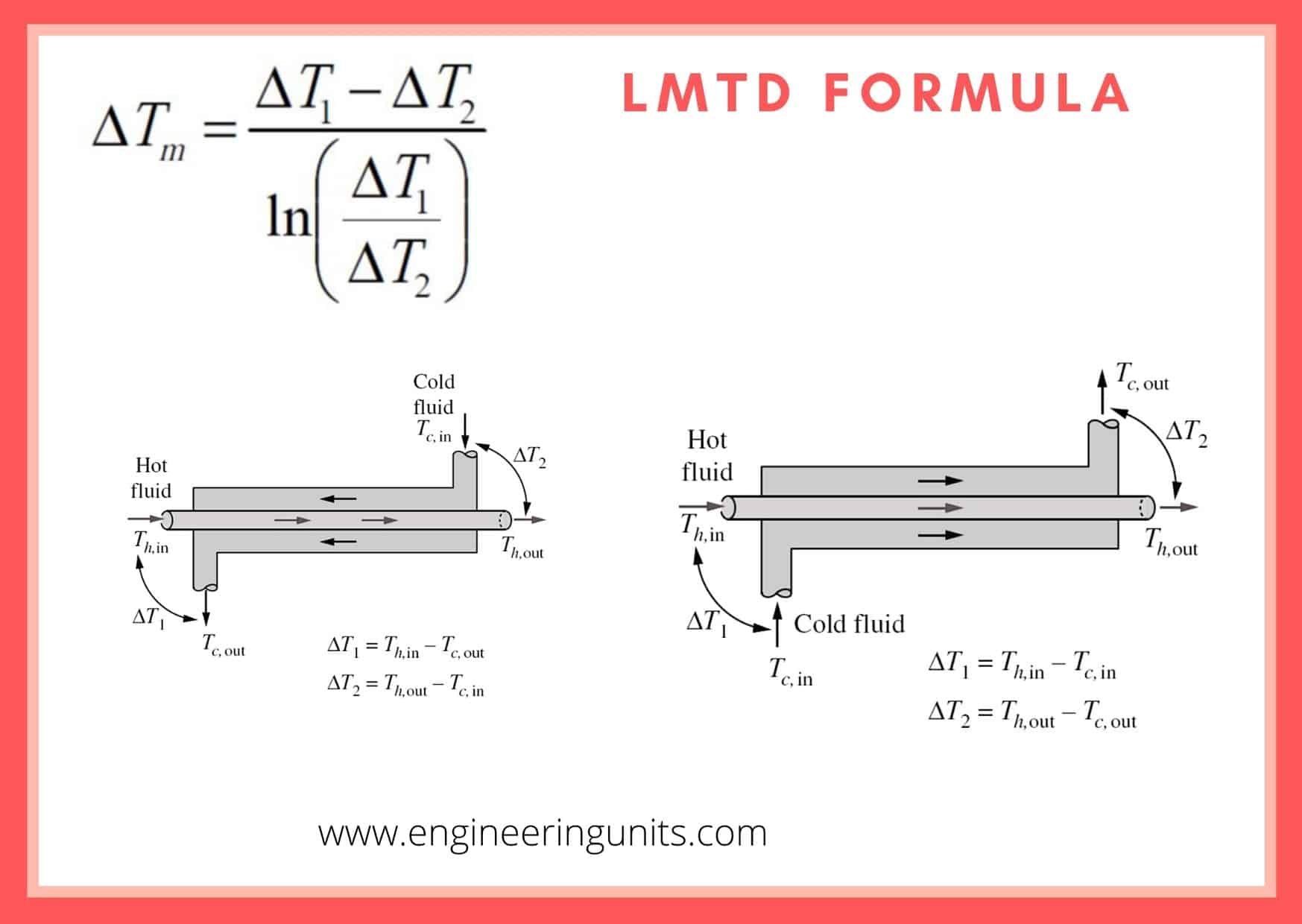
Log Mean Temperature Difference Calculator Engineering Units
0 Response to "Log Mean Temperature Difference Formula"
Post a Comment